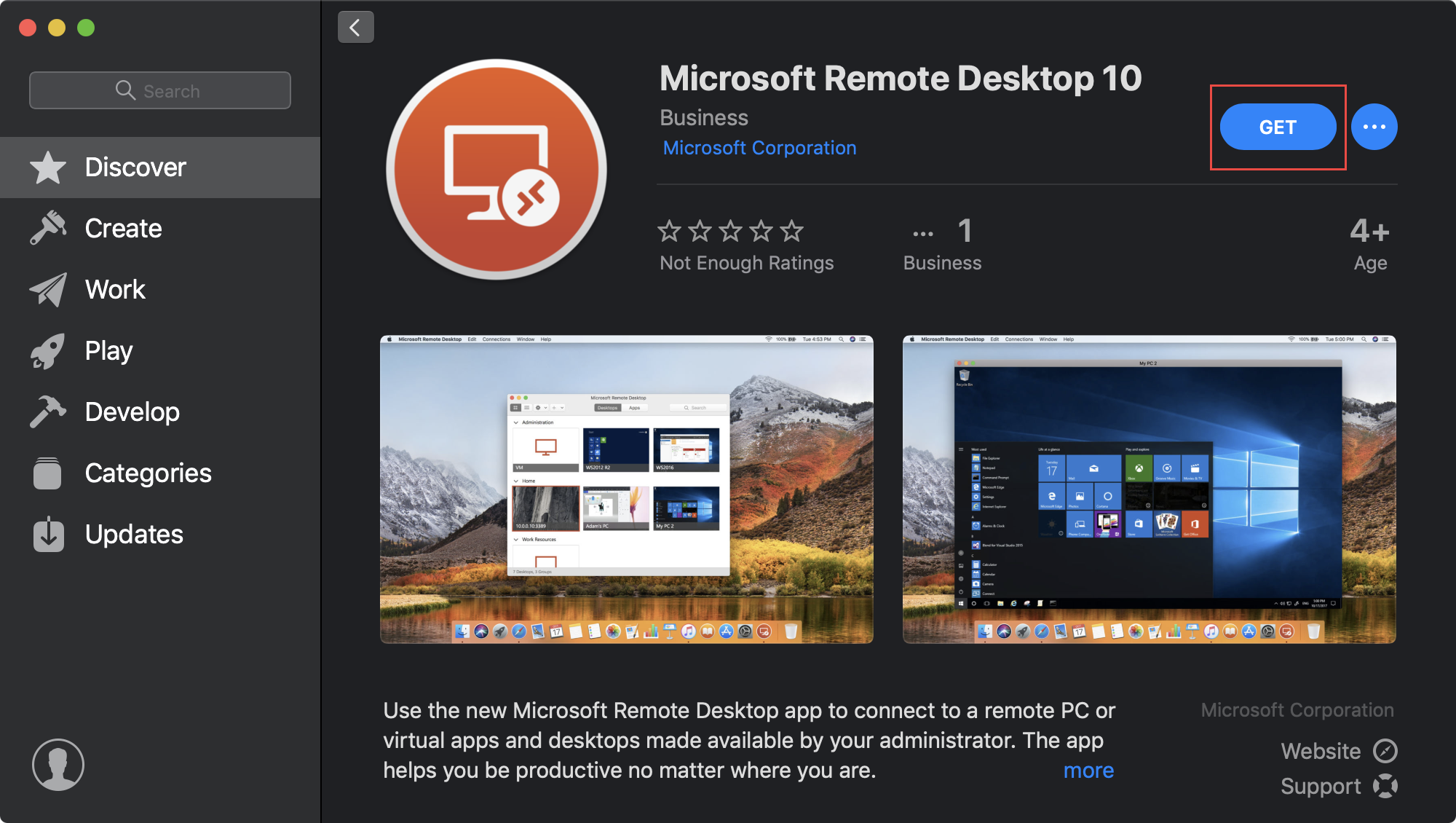
Nearly perfect I have a specific usage case - I work in a multiplatform environment in which I work on the Mac and on the PC. I don't want to keep changing physical keyboards, so despite the fact that the two physical machines are next to eachother beneath my desk, I use remote desktop to view and operate the PC while working on the Mac. Remote Desktop Connection Client for Mac is a Microsoft tool which allows you to connect your Mac to PC Windows machines and other devices. However, Microsoft Remote Desktop on Mac has always had more problems and limitations than the Windows version which is why we don’t recommend using it.
Hello, I am cedrozor the author of Myrtille, a project that started in 2007 as a challenge for fun with former work colleagues, on our spare time. The goal was to provide a native web access, for a simplified user experience, to remote servers and applications. We wanted legacy desktop applications to be as easy to use as a website, accessible from a single URL, making them literally “web apps”.
It was originally the idea of UltraSam, the author of UltraVNC (another well known open source project), who was before that my project manager in a teleconferencing company based in France. But instead of the VNC protocol, we focused more on RDP because the rest of the team (including me) was more into .NET/C# development and we wanted something new in the Windows environment. That said, Myrtille relies on an abstraction layer and could easily integrate VNC or any other protocol (as it was done with SSH).

We started with RDesktop, but moved quickly to FreeRDP when it was released! :)
I have tried to keep the Myrtille footprint into FreeRDP as minimal as possible. Myrtille communicates with FreeRDP through named pipes (IPC), in order to maintain a FIFO data transfer. User inputs (keyboard, mouse, touchscreen, etc.) are captured by the browser (using javascript) and forwarded through the RDP session, while display updates (regions of the screen that have changed) are compressed into PNG, JPEG or WEBP images and sent to the browser (using websocket, server-sent events (HTML5) or even long-polling (HTML4)).
A local RDP client on your laptop can be used to provide a better user experience and is often recommended for Cisco dCloud content.There are many RDP clients available for Windows and Mac, however, the steps in the sections below are for: Microsoft Remote Desktop Connection for Windows; Microsoft Remote Desktop for Mac OS X. RDP on a Mac only works in one direction: you can download the Microsoft Remote Desktop client app from the AppStore and use it to establish a connection from the Mac to a Windows desktop. To setup an inbound remote desktop connection from one Mac.
Mac Rdp Client Settings
Because FreeRDP is a big project, I wanted an easy way to track the Myrtille code within it (whenever I couldn’t have it into separate files). Thus, all the Myrtille code is surrounded by “#pragma region Myrtille” and “#pragma endregion” tags. This is very handy when I need to resynchronize the Myrtille fork of FreeRDP with the FreeRDP repository! Because, of course, I want Myrtille to benefit from the latest features, optimizations and bug fixes from FreeRDP! :) in this process, I may also find and fix bugs in FreeRDP, then inform the FreeRDP team.
In an earlier version (0.9.x), The Windows FreeRDP client (wfreerdp) was written in C++. It’s possible to mix C and C++ code in a single project, so I was able to keep most of the code I wrote years ago and benefit from some C++ improvements over C (OOP, GDI+ image processing, etc.).
I also wanted to have a clean separation of concern between Myrtille and FreeRDP, so each RDP connection spawns a FreeRDP process. This makes it easier to track all active connections and if necessary disconnect one by killing its process.
From the start we decided that we didn’t want any plugin, extension or whatsoever in the browser. It would be a pure HTML/JS/CSS implementation. We also wanted to avoid javascript libraries whenever possible (and reasonable), to avoid useless (and countless) dependencies and keep the code low profiled. For simple tasks (and Myrtille doesn’t require/do anything fancy), I think it’s fine (and even good) to simply use vanilla javascript. Javascript is a powerful language, constantly evolving, and I have fun learning and harnessing it. I’m also a minimalist person who loves to get its hands dirty in the engine to see how things work on a lower level! :p
It was even more difficult back in time (2007), because websockets and canvas (HTML5) weren’t available. We had to rely on XmlHttp requests, long polling and divs (HTML 4), with of course different implementations in different browsers (no typescript back then). IE was still widely used at this time, so we wanted our PoC to run on the first version that supported XmlHttp, namely IE6 (to add even more difficulty!).
That said, that was before SignalR was available to abstract and simplify network communication (automatic and transparent switching of protocols in case one of them is not available or fails). If Myrtille were to start today, I would of course make use of it (in addition to a few other libraries). Another thing I would do would be to use .NET core and the latest new stuff, in order to take Myrtille forward in the future and also have it on multiple platforms (using xfreerdp on Linux, for example). This is planned in fact, and I could use some help for it (any contribution is welcome!). Another option would be to have a commercial version of Myrtille, with a paid license to support these developments (because it’s a lot of work and I now have to earn a living, as an independent developer).
Among the upcoming features, file transfer is the next improvement goal. Microphone support is also planned. Maybe also smart cards after that. A separation of the Myrtille gateway and services is also planned, for an easier configuration of the gateway into a DMZ, and further enhance the security (the installer will allow to select the module to be installed; currently this must be done manually). Still about security, I would like to offer another 2FA out of the box (probably Google Authenticator).
Regarding the user interface, I think Myrtille also needs a little visual rework. The login page, the toolbar will be redesigned with better flat styles, colors and icons.
About deployment and integration (and devops by extension), I would like also to bring more cloud support to Myrtille; Azure obviously, because of its integration within the Microsoft/Windows ecosystem, but not only (Amazon, Google, etc.). Myrtille already have a Docker image, but there are some limitations regarding print and audio. I will also look into that.
Responsiveness is the key to a good user experience. I tried hard to chase for every millisecond I could save in the roundtrip workflow. That’s also why I wanted a lightweight javascript code from the start. The Myrtille gateway is also just that, a link between the browser and FreeRDP, maintaining the correlation between the http and rdp sessions, receiving/forwarding data from/to both sides.
Whenever possible, I try to parallelize the processing. The user inputs and display updates, for example, are asynchronous. You can have a display change resulting from a user action, or not. What is important however, is to maintain the order in which they occur. I decided to use named pipes between the gateway and FreeRDP, because they are FIFO queues and maintain such an order. XmlHttp requests and websocket messages are also delivered in order, and so are long polling DOM injections and server-sent events (SSE).
A path for improvement would be to use hardware accelerated graphics and take advantage of the H.264/AVC encoding supported by FreeRDP. Myrtille actually relies on images (PNG/JPEG/WEBP), generated by GDI+ (win32 API, software), but this could be replaced by a video stream (MP4/OGG/WEBM, etc.), generated by FreeRDP (against hardware, or software when using a VM), and pushed from the gateway to the browser into an HTML5 <video> tag or handled by a modern web API (MediaSource, WebRTC, etc.).
Many thanks to the FreeRDP team for this wonderful project! It is not an easy task when working with such a complex protocol and with so many changes over the years.

If you want to know more about Myrtille and its offered services (support, training, etc.), watch demo/tutorial videos or get in touch, you can consult our website.
 -->
-->Mac Remote Desktop Client
Applies to: macOS 10.12 or later
Important
This content applies to Windows Virtual Desktop with Azure Resource Manager Windows Virtual Desktop objects. If you're using Windows Virtual Desktop (classic) without Azure Resource Manager objects, see this article.
You can access Windows Virtual Desktop resources from your macOS devices with our downloadable client. This guide will tell you how to set up the client.
Install the client
To get started, download and install the client on your macOS device.
Subscribe to a feed
Subscribe to the feed your admin gave you to get the list of managed resources available to you on your macOS device.
To subscribe to a feed:
- Select Add Workspace on the main page to connect to the service and retrieve your resources.
- Enter the Feed URL. This can be a URL or email address:
- If you use a URL, use the one your admin gave you. Normally, the URL is https://rdweb.wvd.microsoft.com/api/arm/feeddiscovery.
- To use email, enter your email address. This tells the client to search for a URL associated with your email address if your admin configured the server that way.
- To connect through the US Gov portal, use https://rdweb.wvd.azure.us/api/arm/feeddiscovery.
- Select Add.
- Sign in with your user account when prompted.
After you've signed in, you should see a list of available resources.
Once you've subscribed to a feed, the feed's content will update automatically on a regular basis. Resources may be added, changed, or removed based on changes made by your administrator.
Next steps
To learn more about the macOS client, check out the Get started with the macOS client documentation.
